Anesthesia is essential for modern surgery and medical procedures, allowing patients to undergo interventions safely and pain-free. There are several types of anesthesia, each tailored to the procedure, patient needs, and desired effects. Understanding the differences helps patients feel informed and prepared for their care.
General Anesthesia
General anesthesia induces complete unconsciousness and a lack of sensation throughout the body. It is used for major surgeries where pain control and immobility are critical.
How It Works
- Administered through inhaled gases or intravenous drugs
- Suppresses central nervous system activity
- Blocks pain perception and awareness
Monitoring and Safety
- Continuous monitoring of heart rate, blood pressure, oxygenation, and breathing
- Use of ventilators if the patient cannot breathe independently
- Adjustments made in real time by the anesthesiologist
Benefits
- Complete pain relief
- Immobility for surgical precision
- Amnesia for the procedure
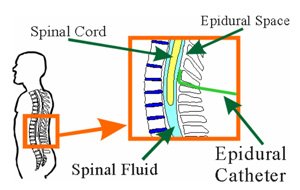
Regional Anesthesia
Regional anesthesia numbs a larger part of the body without affecting consciousness. It includes spinal, epidural, and peripheral nerve blocks.
How It Works
- Local anesthetic is injected near specific nerves
- Blocks pain signals from reaching the brain
- Patient may remain awake or lightly sedated
Common Uses
- Childbirth (epidural)
- Limb surgeries
- Some abdominal procedures
Benefits
- Reduced systemic drug exposure
- Effective pain relief with fewer side effects
- Can be combined with sedation for comfort
Local Anesthesia
Local anesthesia targets a small area, numbing only the specific site of the procedure.
How It Works
- Direct injection or topical application of anesthetic
- Blocks nerve signals in a limited area
- Patient remains fully awake
Common Uses
- Dental procedures
- Minor skin surgeries
- Biopsies
Benefits
- Minimal drug exposure
- Quick onset and recovery
- High safety profile
Sedation (Conscious Sedation)
Sedation is sometimes considered a separate category:
- Minimal Sedation: Patient relaxed but fully awake
- Moderate Sedation: Patient may be drowsy but responds to verbal commands
- Deep Sedation: Patient near unconsciousness but can still be aroused
Sedation is often combined with local or regional anesthesia to reduce anxiety and discomfort.
Choosing the Right Type
Anesthesiologists determine the type of anesthesia based on:
- Type and duration of surgery
- Patient age and health
- Pain management needs
- Potential risks and side effects
FAQs
1. Which anesthesia is safest?
All types are safe when administered by trained professionals. The choice depends on the procedure and patient factors.
2. Can regional anesthesia be used for major surgeries?
Yes, in combination with sedation, regional techniques can be sufficient for many procedures.
3. Does local anesthesia hurt?
The injection may cause slight discomfort, but the area becomes numb quickly.
4. Can patients remember the surgery under general anesthesia?
Generally, no. Amnesia is a key effect of general anesthesia.
5. How long does it take to recover from different anesthesia types?
Local anesthesia has minimal recovery time, regional anesthesia may take a few hours, and general anesthesia can take several hours depending on the drugs used.